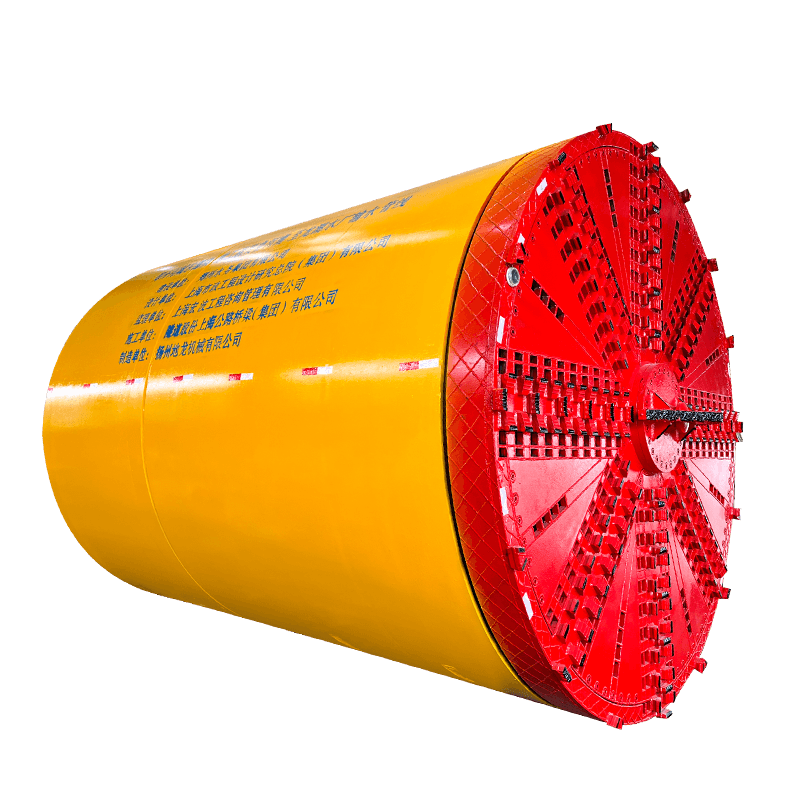
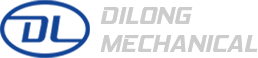The Pipe Jacking Machine is a cornerstone of modern trenchless technology, an engineering marvel that allows for the installation of underground pipelines without the need for extensive, disruptive open-cut excavation. This method has revolutionized the way critical infrastructure—such as sewer lines, water mains, and utility conduits—is laid beneath roads, railways, buildings, and environmentally sensitive areas.
How the Pipe Jacking Machine Works
The core principle of the technique involves hydraulically advancing pre-cast pipe sections through the ground from a starting pit, known as the jacking pit, toward a reception pit.
The Components and Process
The primary elements involved in this sophisticated operation are:
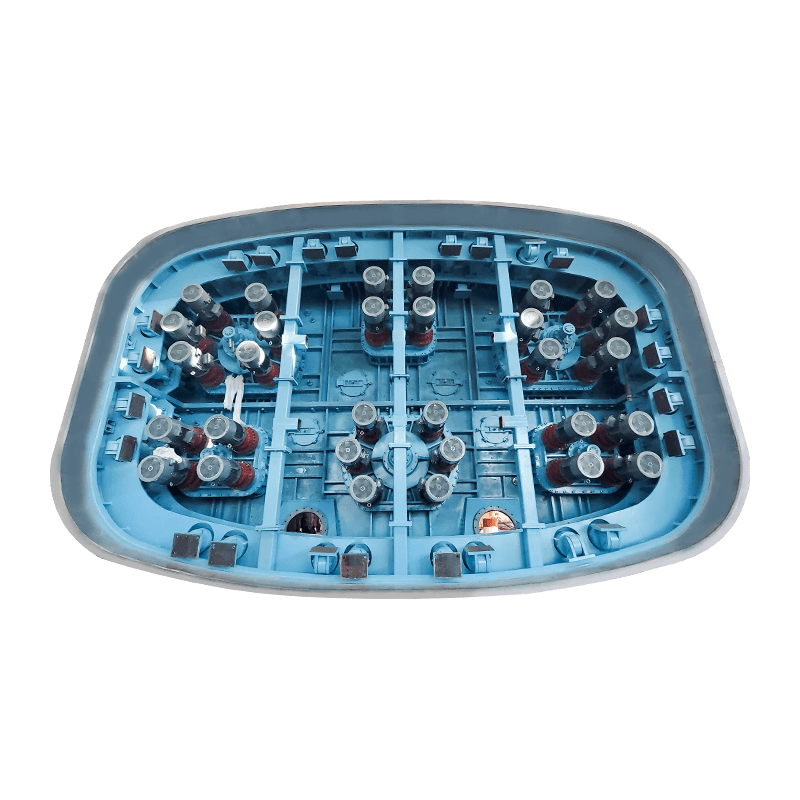
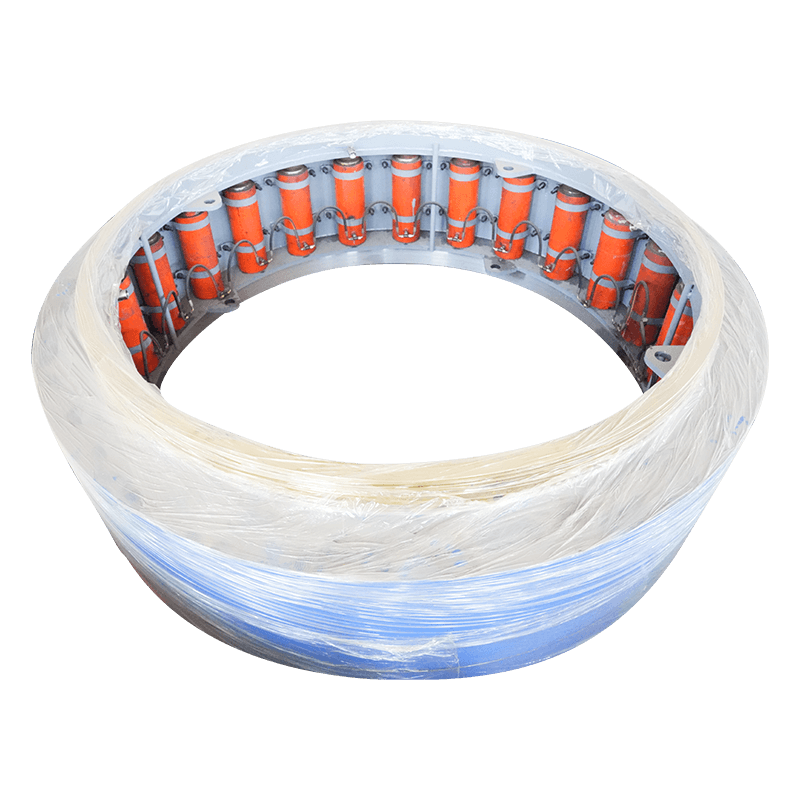
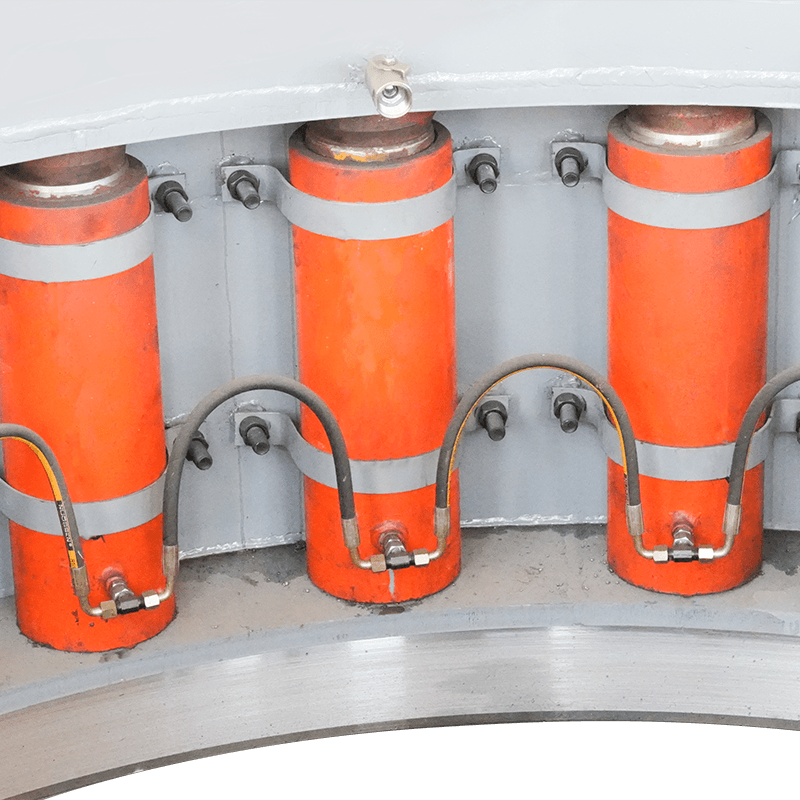
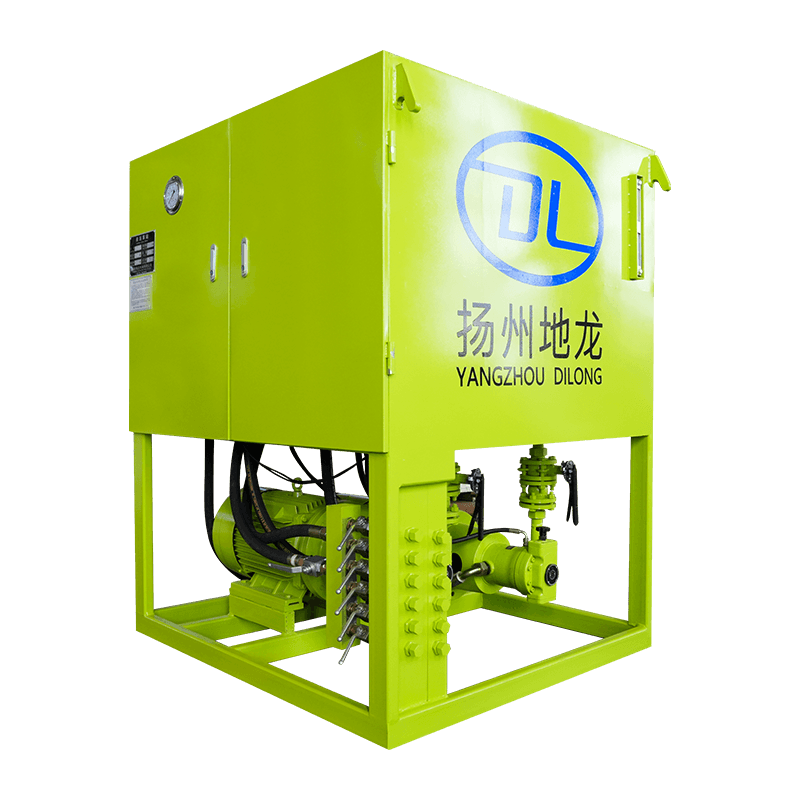
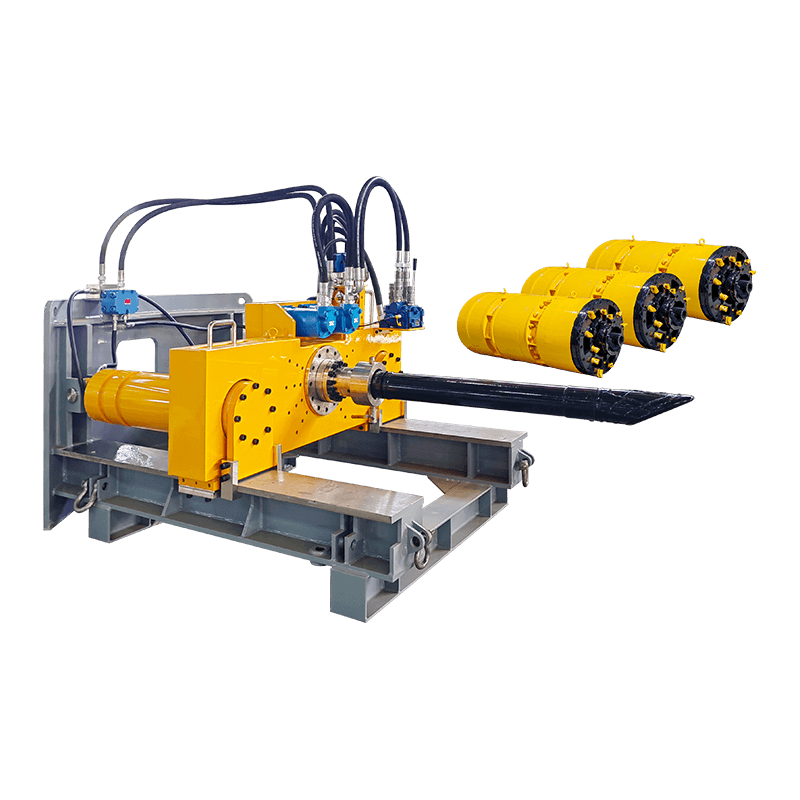
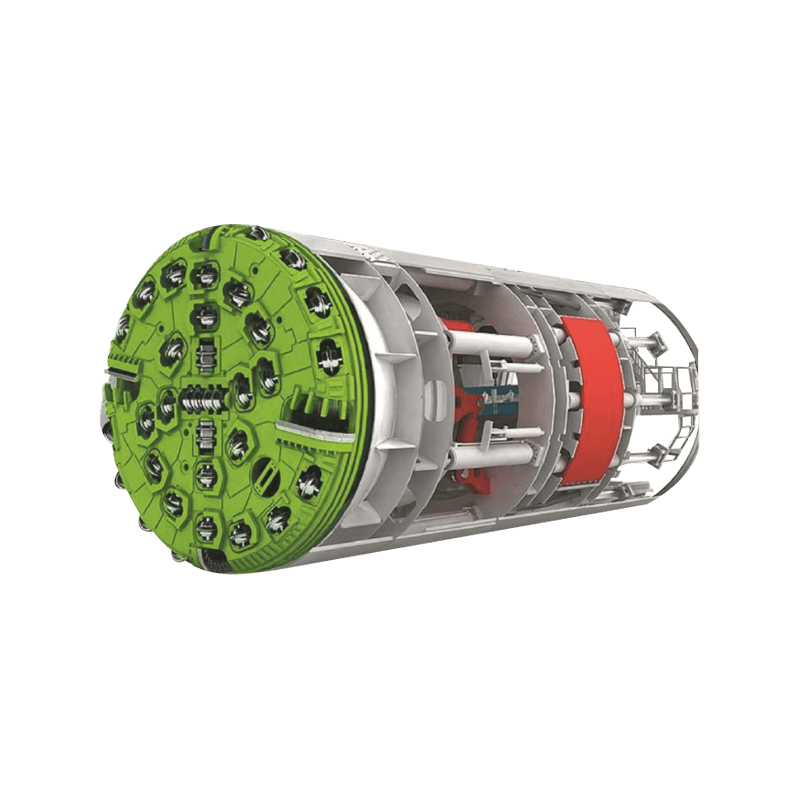
- Jacking Frame: Located in the jacking pit, this is the main power source. It houses a series of high-capacity hydraulic rams that apply the necessary thrust to push the pipe string forward.
- Thrust Ring: A structure positioned between the hydraulic rams and the lead pipe section to distribute the jacking force evenly across the pipe’s circumference, preventing localized damage.
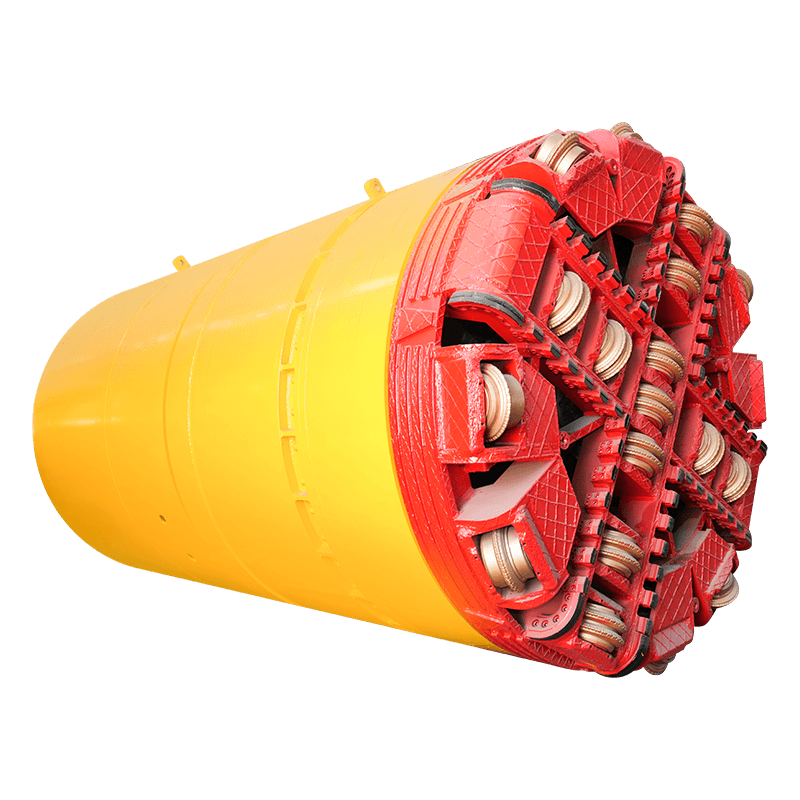
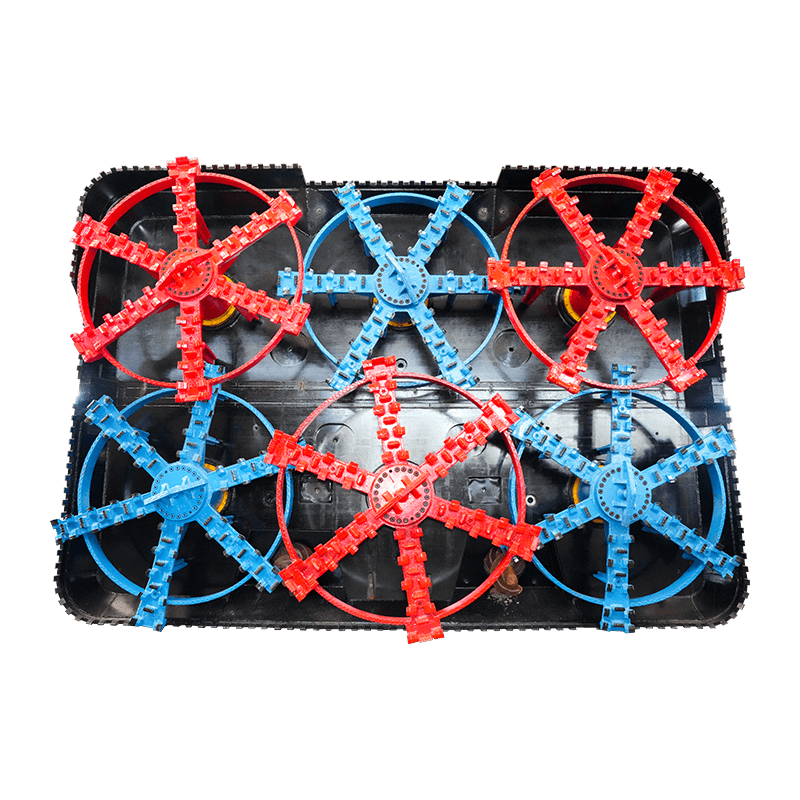
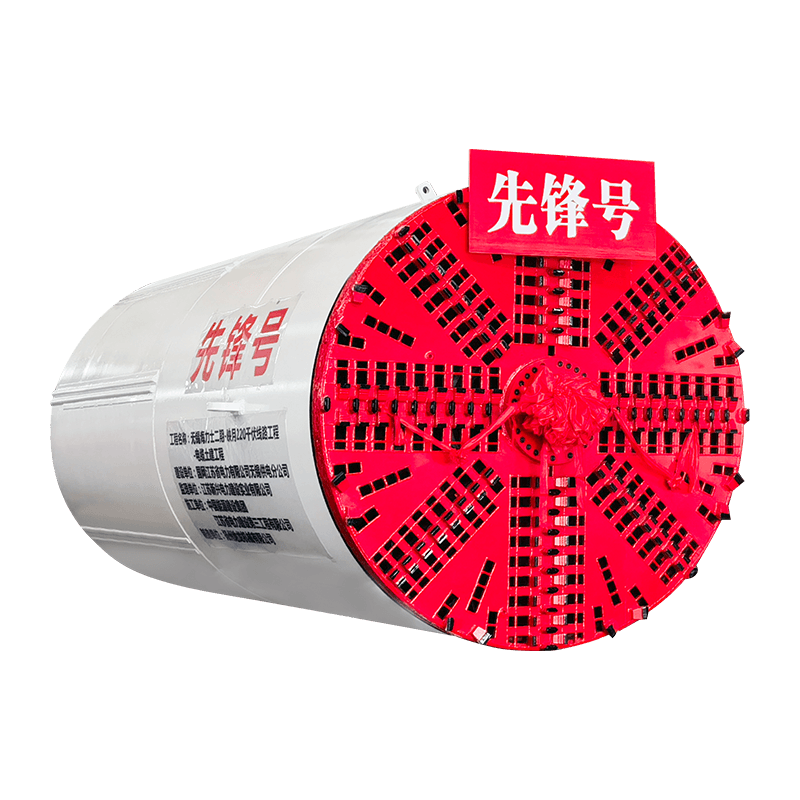
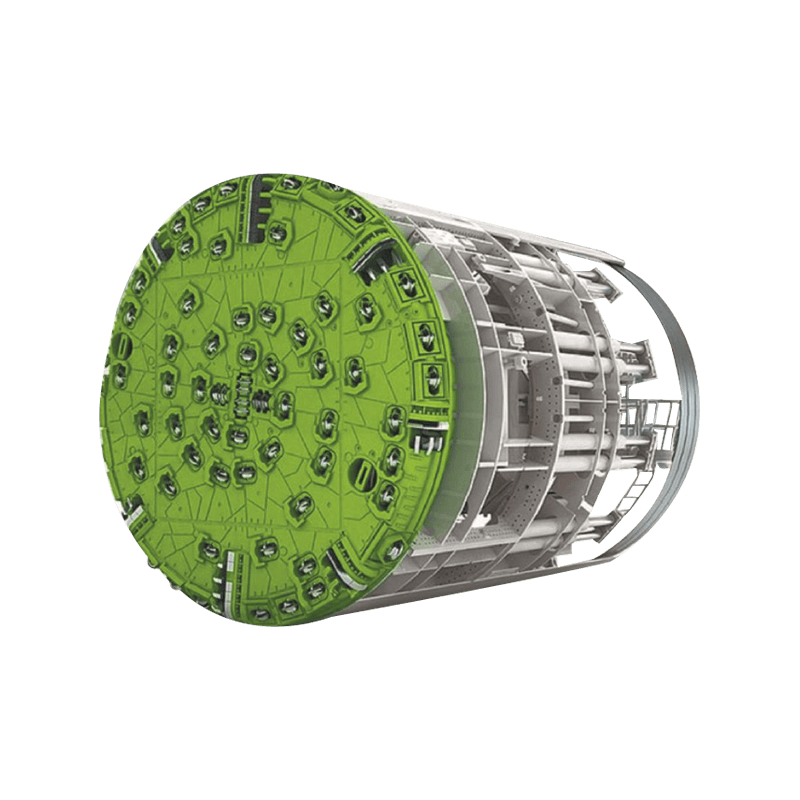
- Tunnel Boring Machine (TBM) or Shield: At the front end of the pipe string, a specialized cutting head or shield is used to excavate the soil. For larger or more complex projects, this TBM is often a Microtunnel Boring Machine (MTBM), which is guided by a laser-based surveying system to ensure precise line and grade control.
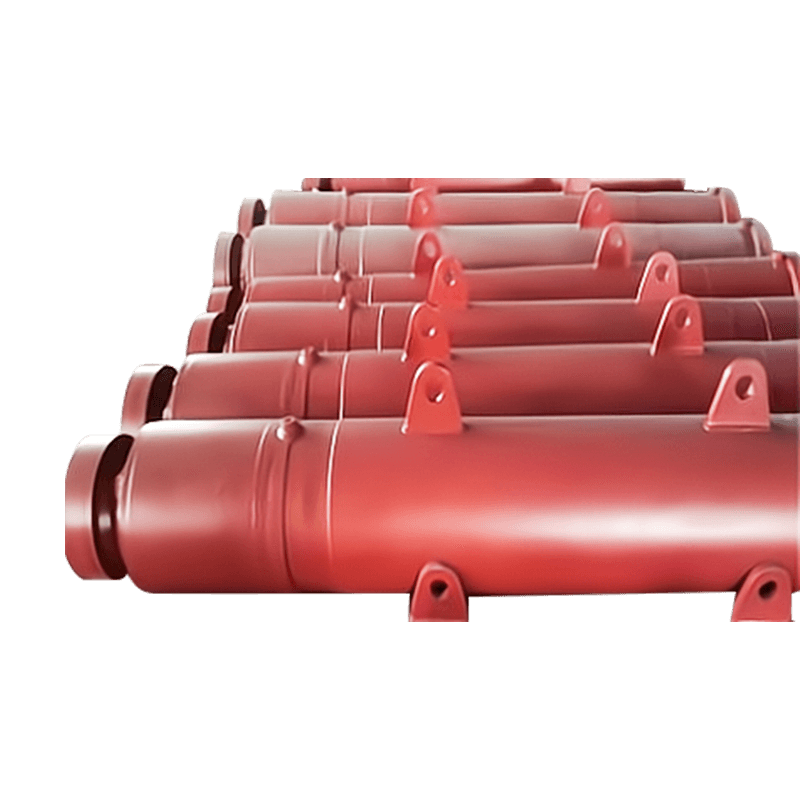
- Pipe String: The sequential sections of pipe that are pushed into the ground. Once a section is fully advanced, the hydraulic rams are retracted, a new pipe is lowered into the jacking pit, and the process repeats.
- Lubrication System: A crucial element where a bentonite or polymer-based slurry is injected into the annular gap (the space between the excavated tunnel and the exterior of the pipe) to reduce friction, thereby minimizing the total required jacking force.
The operation is typically remotely controlled and monitored from the surface, allowing for real-time adjustments to steering and ground conditions.
Advantages of Trenchless Technology
The adoption of the Pipe Jacking Machine technique over traditional open-cut methods offers significant advantages, making it the preferred choice for urban and challenging environments:
- Minimized Surface Disruption: By eliminating the need for long trenches, the method dramatically reduces traffic congestion, noise pollution, and disturbance to businesses and residents.
- Depth and Distance Capability: It is highly effective for installing pipes deep beneath the surface and over long distances, which is difficult or impossible with conventional methods.
- Structural Integrity: The installed pipes are subject to less stress during the process compared to pipes laid in an open trench, potentially leading to a longer service life.
- Environmental Protection: It avoids damage to ecologically sensitive areas, reduces the generation of spoil material, and minimizes the impact on groundwater tables.
- Accuracy: Modern guidance systems allow for an extremely high degree of accuracy in both the horizontal and vertical alignment of the pipeline.
Applications and Project Scope
The versatility of the Pipe Jacking Machine enables its use across a diverse range of infrastructure projects:
| Project Type | Typical Pipe Diameter Range | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Sanitary & Storm Sewers | 600 mm to 3,000 mm | Crossing beneath major highways, rivers, or dense city blocks. |
| Water Mains | Various | High-pressure lines where minimal leakage risk is critical. |
| Utility Conduits | Smaller diameters | Installation of electrical or telecommunication cables. |
| Pedestrian Tunnels | Larger diameters | Underpasses beneath busy transport hubs. |
In conclusion, the Pipe Jacking Machine represents a powerful intersection of mechanical and civil engineering. Its capacity to install robust infrastructure with precision and minimal disruption solidifies its role as a fundamental technology for building and maintaining the essential hidden networks of the modern world.





 English
English  русский
русский  عربى
عربى